Reverse Logistics: Key to Sustainability and Efficiency in the Modern World
Introduction
In my sessions with clients or during supply chain management training, I often ask: "How many supply chains do you have in your organization?" Often, more than half say they have only one. However, when delving into product returns, they realize the existence of reverse logistics, highlighting at least two chains. Once marginal, reverse logistics is now essential for companies aiming for sustainability and efficiency. With a global market valued at $555 billion in 2021 and projected to reach $831.3 billion by 2030, according to Straits Research, this sector is experiencing an annual growth of 5.18%. This field covers the return of products for repair, recycling, or disposal, crucial in the circular economy and reducing environmental impact.
Fundamentals of Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics is distinctly different from traditional logistics in its focus on product returns. This process encompasses the management of goods returns but goes beyond: it also includes the recycling of materials and packaging, the remanufacturing of used products, their remarketing, and their final disposition. This approach is of paramount importance in sectors such as electronics, distribution, and retail, where the rapid pace of product renewal calls for both efficient and responsible returns and waste management.
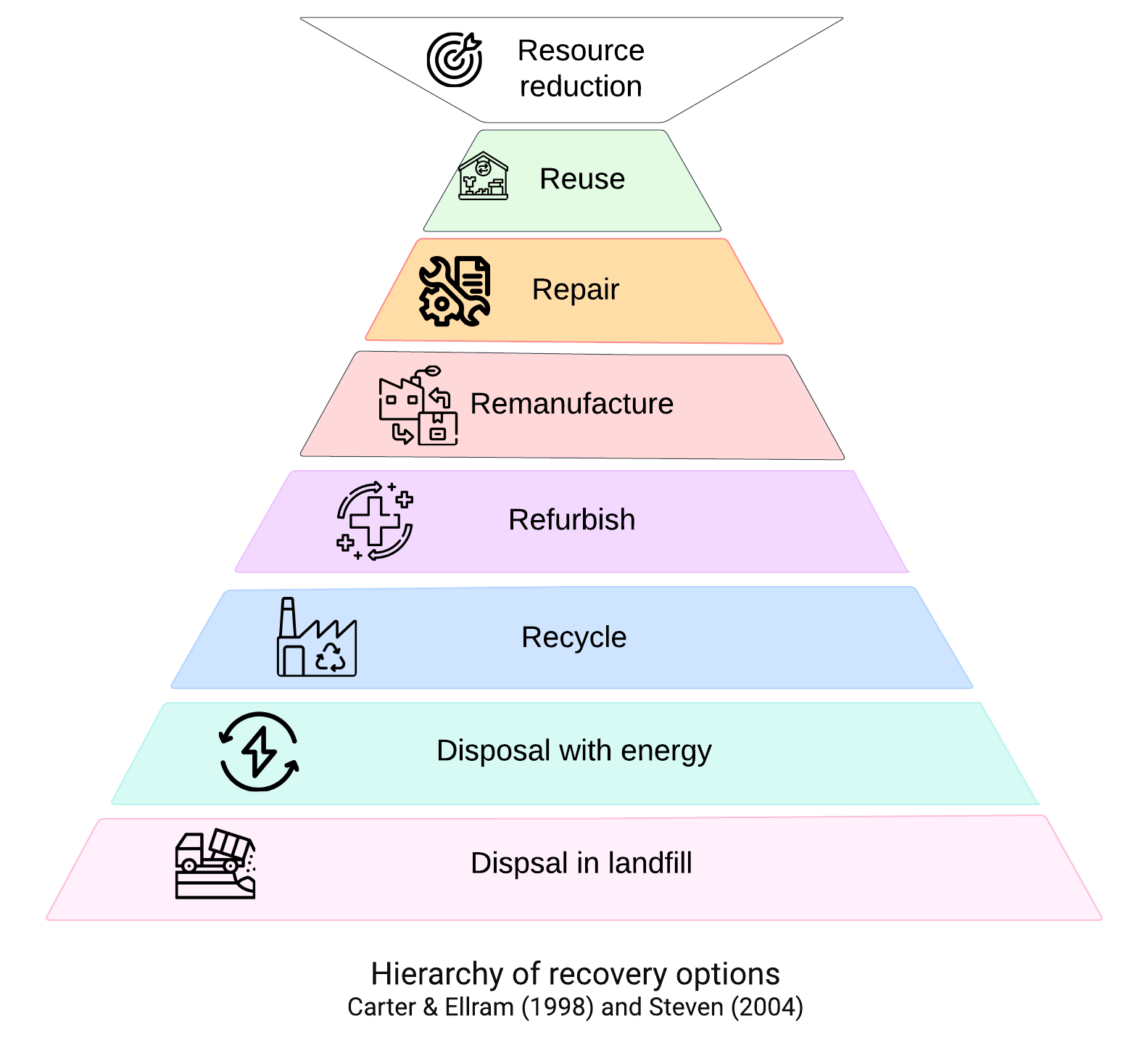
The hierarchy of recovery options, illustrated in the figure alongside, provides a decision-making framework for designing return policies and end-of-life product management. From resource reduction to landfill disposal, each level of this pyramid guides companies towards the most sustainable and efficient practices.
It is crucial to develop return policies that are not only clear, well-defined, and easily accessible to customers but also aligned with these recovery principles. These policies play a key role in managing customer expectations and simplifying the return process. The discussion on integrating return fees is increasingly present in the industry, and although this practice may be controversial, it has the potential to discourage unnecessary returns while offsetting associated logistical costs.
Benefits of Reverse Logistics
The benefits of reverse logistics are manifold.
For customers, reverse logistics enables more flexible and efficient return management, increasing their satisfaction. Customers benefit from simplified return processes and can access repair services or have the option to return defective products, which improves their overall shopping experience. Easy returns and liberal return policies, influenced by online commerce giants, have made returns more common, transforming the return experience into a positive aspect of the customer-seller relationship.
For retailers, reverse logistics represents an opportunity to improve inventory management and recover some value from returned products. This can include reselling products returned in perfect condition, repairing or refurbishing products for the market, or recycling materials for use in new products. Moreover, effective return management can help reduce operational costs and increase profit margins. Companies like H&M and Apple have integrated reverse logistics into their business models by collecting used products or devices for recycling, thus showing a commitment to sustainability and reducing production costs.
For manufacturers, reverse logistics helps maintain a circular economy by reusing and recycling materials, thus contributing to environmental sustainability. It also helps manufacturers comply with government regulations on recycling and waste management. By collecting returns directly from consumers or through retailers, manufacturers can reduce waste, improve production efficiency, and even discover opportunities to enhance product quality and innovation by analyzing return patterns.
Finally, on an environmental level, it allows for a significant reduction in companies' ecological footprint by promoting the recycling and reuse of products. Innovative bio-recycling solutions, like that of Carbios, which enables the recycling of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), will allow manufacturers and users to recover the necessary monomers to make recycled PET (r-PET) of the same quality as PET derived from oil. Quebec-based Biozyme technologies are in line to acquire a Carbios license to implement this technology in Quebec.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its advantages, reverse logistics presents notable challenges. Logistical costs and the complexity of return management are major obstacles. To overcome them, emerging solutions include the adoption of innovative technologies to optimize return flows and product processing. Notable examples include the use of artificial intelligence to predict returns and automate sorting and repairing of products.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of reverse logistics is marked by innovation and the adoption of new technologies.
Return management software (RMS) to streamline the process from the receipt of returns to their final treatment, including their sorting. The automation of sorting or reconditioning of returned products helps reduce costs and speed up the process. Finally, artificial intelligence is already transforming return and recycling processes, while blockchain promises to improve the traceability and transparency of returned products.
Reverse logistics plays a crucial role in the transition to a circular economy. Companies like IKEA are committing to this path by taking back and recycling their products to reduce waste. IKEA Sustainability Report 2020.
At the same time, the evolution of business models towards deposit, rental, and subscription systems (Decathlon in Europe) reveals new ways to reduce waste and encourage product reuse.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reverse logistics is an essential component of future-oriented corporate strategies. Its importance will grow as environmental and economic concerns prompt companies to rethink their supply chains. Adopting and innovating in reverse logistics is not just a matter of environmental responsibility; it is also a strategic lever for improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
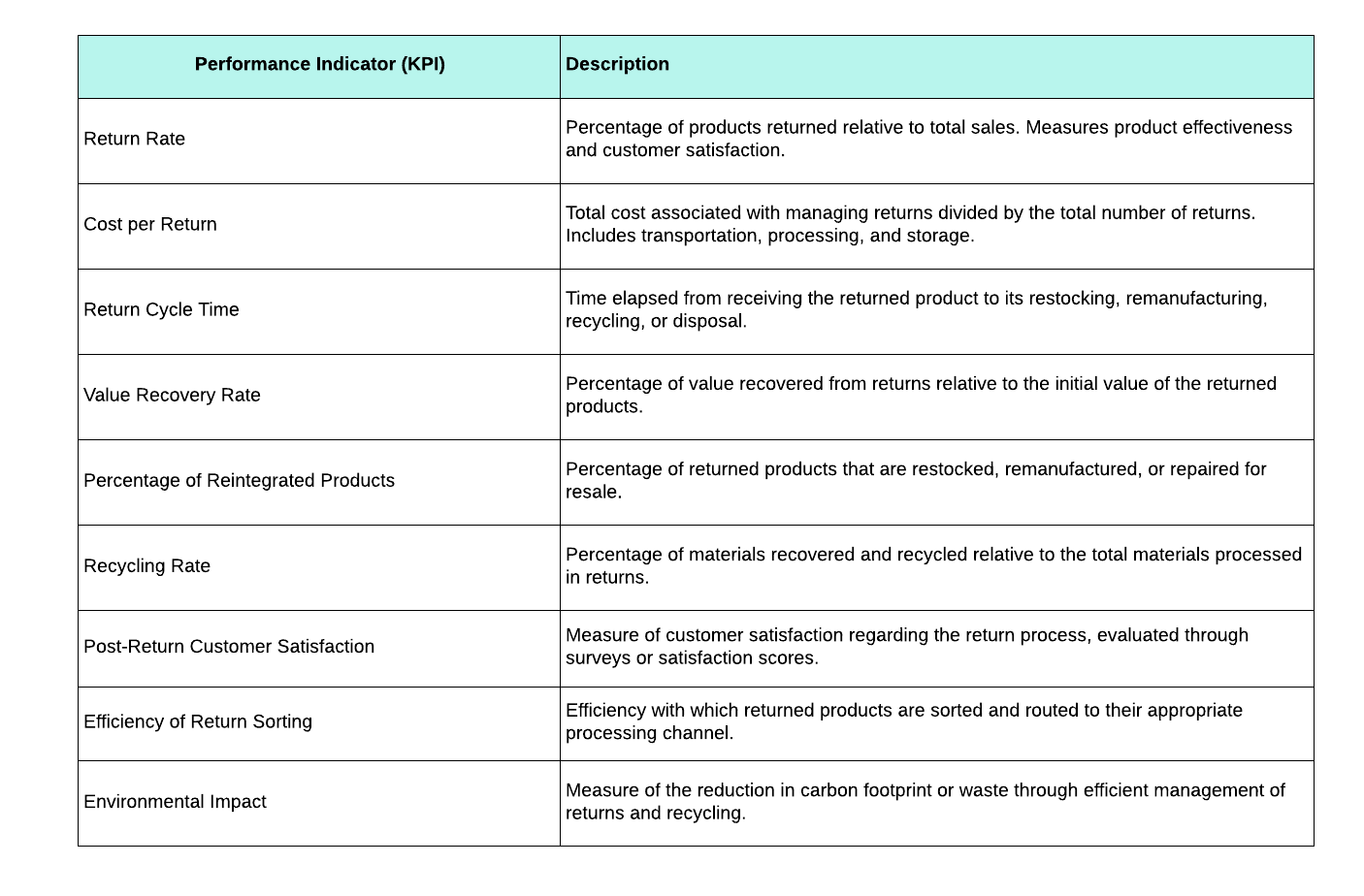
List of key indicators for managing reverse logistics.
Do you have needs to help you with your reverse logistics? Contact us